Flat Feet
The Condition
A decreased medial arch height is commonly referred to as ‘flat foot’ deformity. The change in foot position and arch height in adults is often found to be associated with posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD). The posterior tibial tendon is a soft tissue structure that helps maintain stability and support to the arch of the foot. The degeneration of this tendon over time leads to a decrease in the arch height and the formation of arthritis. If left untreated, this problem can cause proximal limb pain and lower back pain.
The Treatment
Pain usually prompts patients to seek treatment. Unfortunately, the onset of pain signals the presence of damage to the tendon and surrounding tissue. Early identification of the deformity and the use of custom foot orthotics can be a beneficial prophylactic treatment method.
A thorough physical examination of the foot and ankle should be performed to assess overall muscle strength and function. Plain film radiographs (X-Rays) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can assist in identifying the severity of the condition. In some cases, computer assisted tomography scans (CT) and musculoskeletal ultrasound may also be used to evaluate the integrity of the tendon and bone. Treatments are customized based upon patient needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
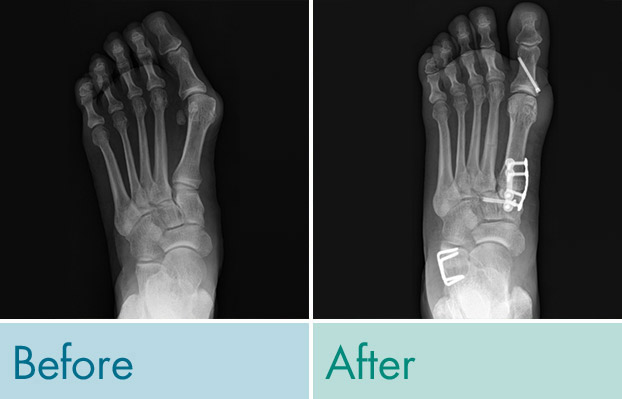
Before & After Photos
Articles
A Patient’s Guide to Natural Healing: Autologous Conditioned Plasma (ACP)This brochure further explains the platelet rich plasma prolotherapy treatment currently offered at JCMG Podiatry.